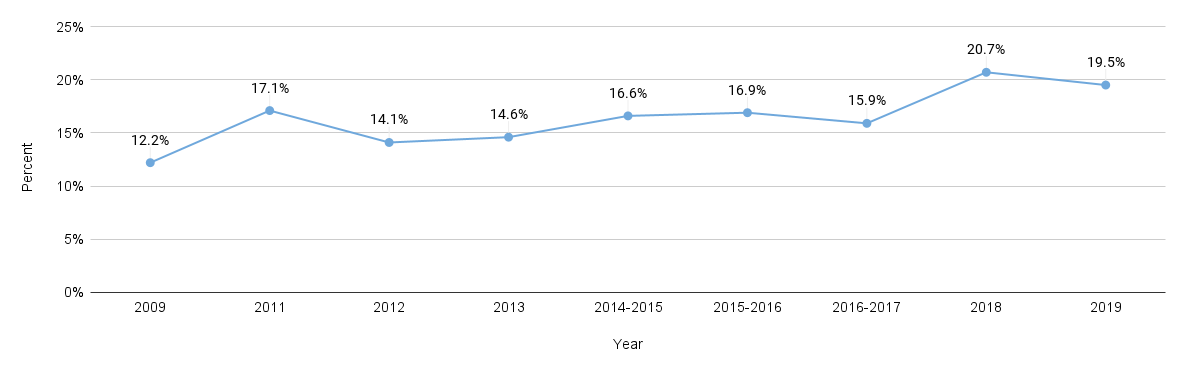
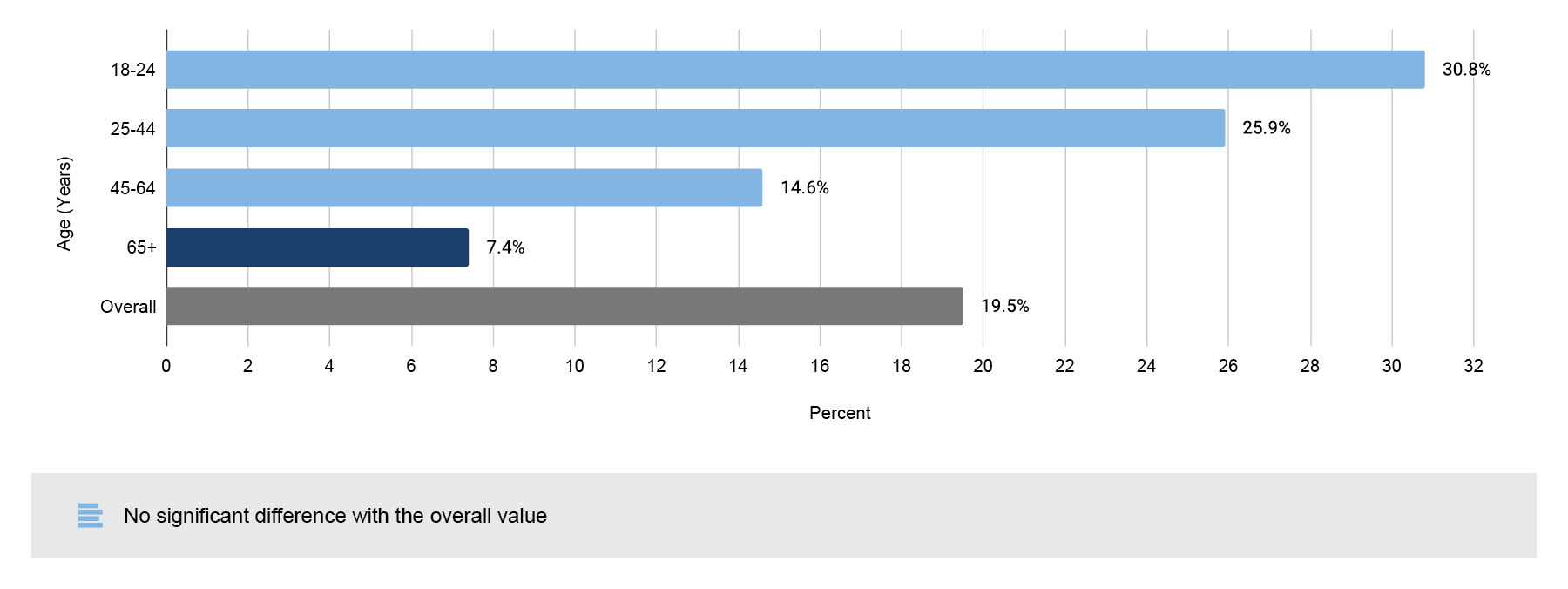
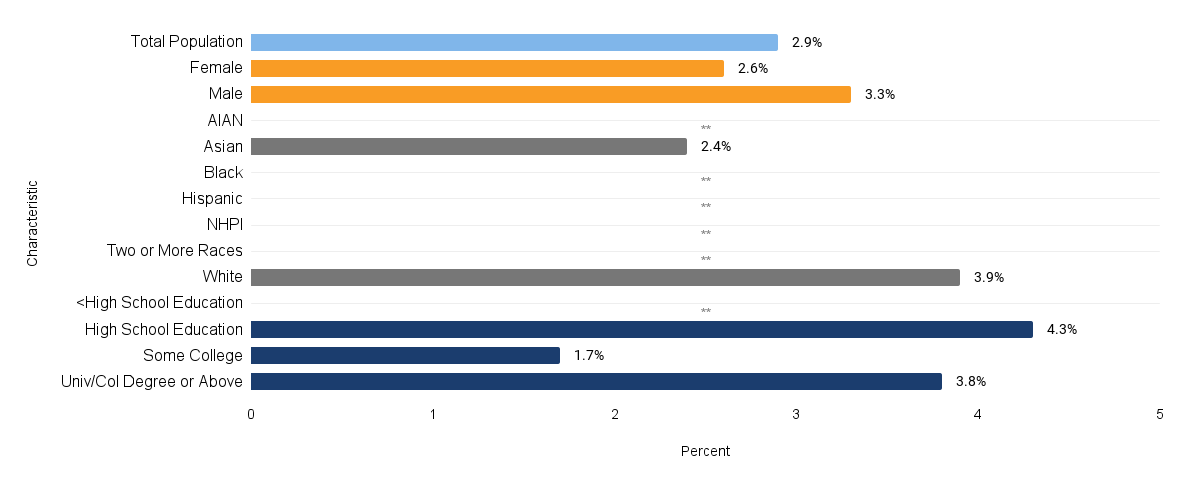
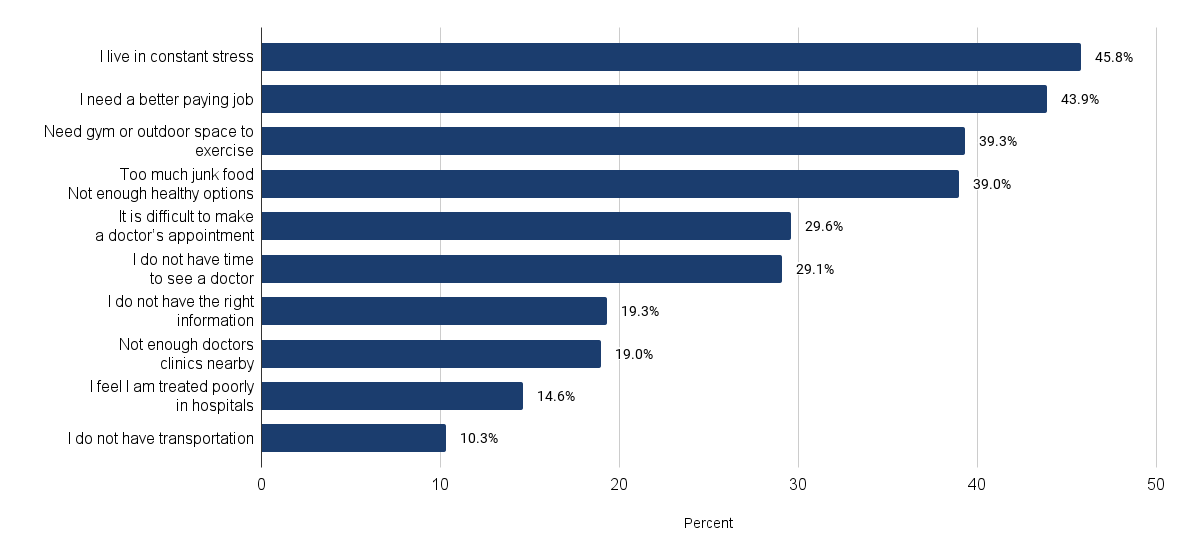
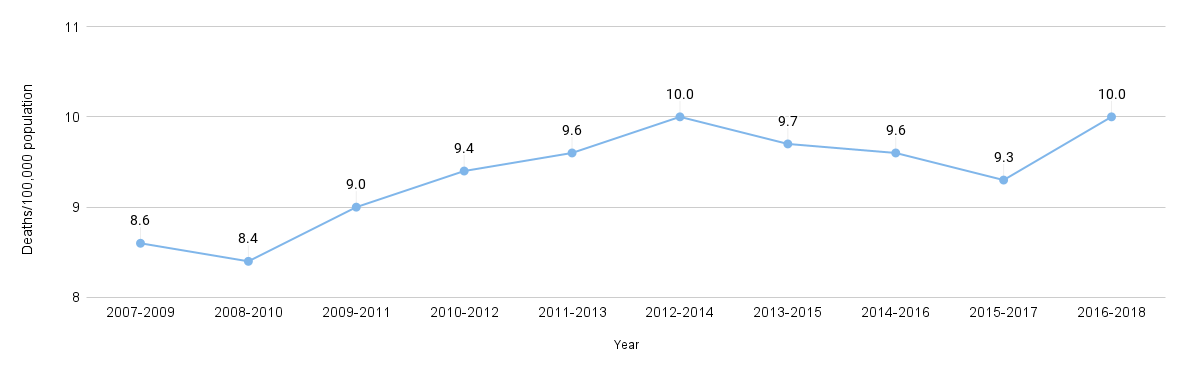
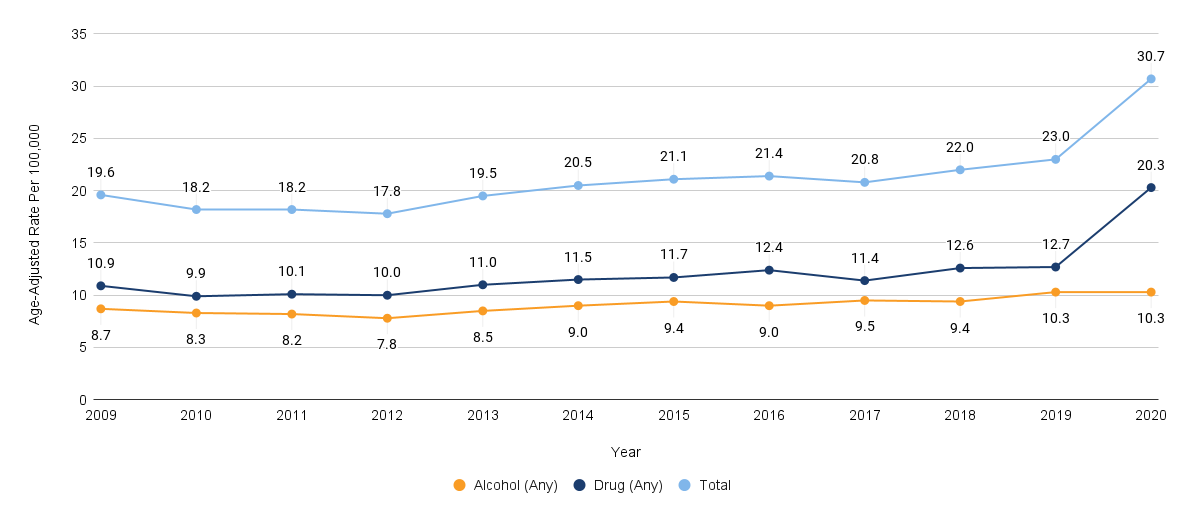
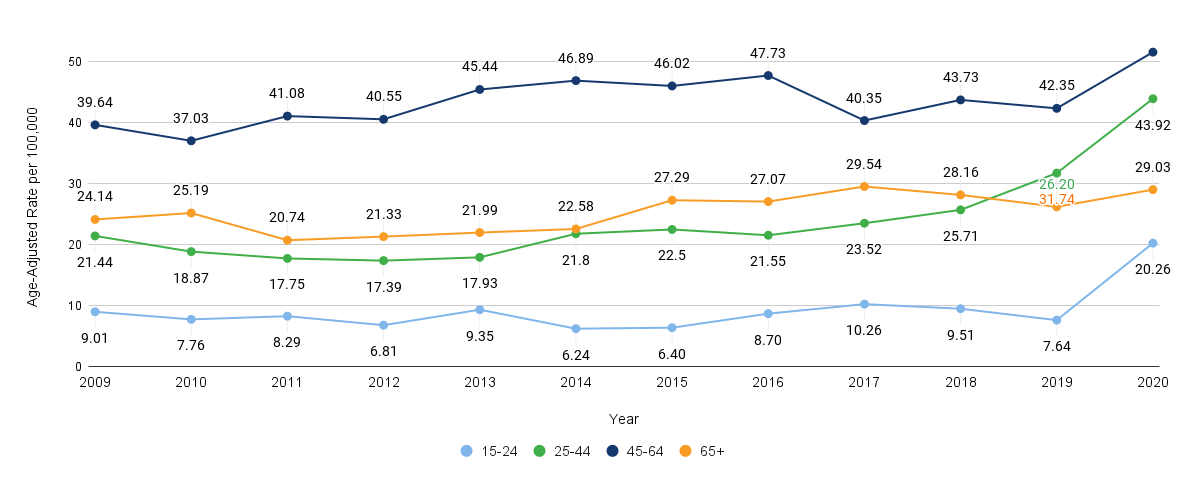
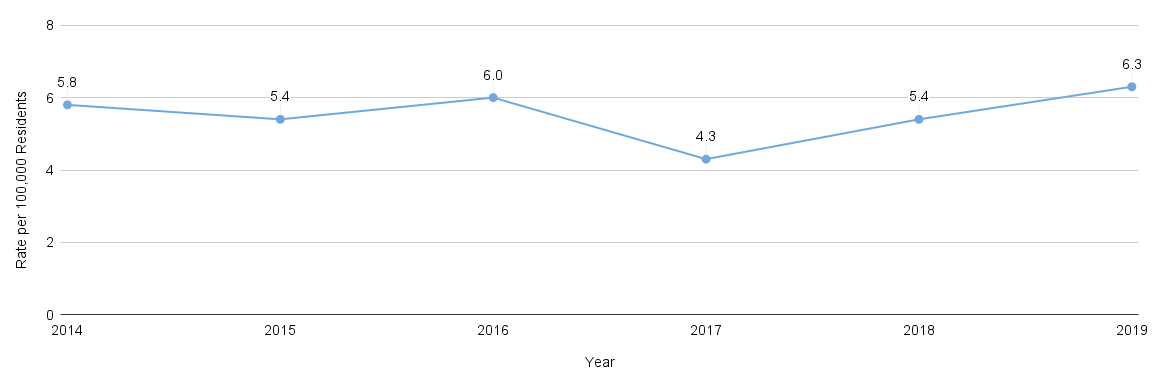
According to the Hoag 2022 Community Needs Assessment report, behavioral and mental health was identified as a significant concern in the community. Nearly a quarter (23%) of the community survey respondents indicated that the most pressing health need in their household was emotional well-being. Furthermore, when asked about the most pressing health need in their communities, focus group and interview participants overwhelmingly cited behavioral health.
In the Orange County Mental Health Services Act (MHSA) 2020 survey, it was found that mental health and substance use disorders were among the top priorities in seven service areas: behavioral health system navigation, outreach & engagement, outpatient treatment, crisis services, non-emergency treatment, supportive services, and stigma & discrimination reduction.